We continue with our journey through Pregnancy Week by Week to stop at the week 4 of pregnancy, or week 2 of gestation. As you know, the duration of pregnancy is 40 weeks from the date of the last menstruation (FUM) and 38 weeks from conception.
In the week 4 of pregnancy, four to seven days after fertilization, the embryo implantation on the walls of the mother's womb, where it will continue to develop until the day of her birth.
Embryo Implantation
After fertilization in the uterine tube, the blast, set of embryonic cells formed from the union of the ovule and sperm, descends into the uterus cavity. There it produces some extensions that will allow it to adhere to the mucosa and "bury" in the endometrium, it is what is known as embryonic implantation.
After the blast is implanted in the endometrium, it is when you start talking about a embryo.
Fourteen days after fertilization, the embryo is firmly nested in its new home. That is where a new being will grow and develop.
Implantation bleeding
When implantation occurs, the body sends chemical signals to prevent menstruation from occurring.
On some occasions, when the embryo is implanted in the uterus, the endometrial tissue erodes causing slight bleeding that, when coinciding with the time when the period should be lowered, can be confused with menstruation. This bleeding is known as implantation bleeding.
The loss caused by the nesting of the fertilized egg in the wall of the uterus can last from one to three days, is usually lighter than bleeding due to menstruation and darker. Sometimes it is just a drop of blood and at other times it can be confused with a light menstruation.
Week 4 of pregnancy

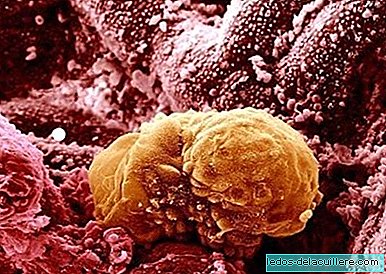
In the embryo it has barely two weeks old and measures half a millimeter. It still has no human appearance, but you can distinguish the bumps that will later be the baby's head and body.
The embryo at this stage is composed of three layers that will give rise to the different tissues and organs of the body. He ectoderm (the outer covering) that will lead to the formation of the nervous system, the mesoderm, (intermediate cover) that will be in charge of forming the majority of internal organs as well as the reproductive organs and the circulatory system, bones, muscles and cartilage, and the endoderm (internal cover), which will give rise to the respiratory and digestive system.
The neural tube and spinal cord belonging to the baby's central nervous system begin to form. The placenta is also formed, which will be responsible for transmitting nutrients and oxygen to the baby throughout the pregnancy. Meanwhile, that function is fulfilled by the yolk sac, an embryonic annex, which will disappear in the coming weeks.
Pregnancy test

Surely in this week or in the next few days, seeing that bleeding from menstruation does not occur, you will take the pregnancy test.
To make your result more reliable, you should do it with the first morning urine which is the one with the highest concentration of the pregnancy hormone, chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG), and expect to have a delay of at least one day.
Some women begin to feel the first signs of pregnancy, such as dizziness, nausea and generalized tiredness. There are even those who by their own intuition realize that they are pregnant before confirming it with a test.
It is very important that if you have not done them before, you start taking a daily supplement of 400 mg of folic acid. Ideally, start taking it at least a month before becoming pregnant to ensure that the body has a sufficient reserve of this essential vitamin that prevents defects in the fetus.
Next Week: Week 5 of pregnancy
Photos | Bradley Smith in The Multi-Dimensional Human Embryo, BrownGuacamole In Babies and more | Pregnancy week by week: from conception to birth